2024-cryptoctf-wp
Easy
alibos
题目描述:1
Alibos, a classic cryptographic algorithm, is designed to safeguard non-sensitive data, providing a reliable solution for routine information protection.
题目:
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 |
output:1
2pkey = 8582435512564229286688465405009040056856016872134514945016805951785759509953023638490767572236748566493023965794194297026085882082781147026501124183913218900918532638964014591302221504335115379744625749001902791287122243760312557423006862735120339132655680911213722073949690947638446354528576541717311700749946777
enc = 6314597738211377086770535291073179315279171595861180001679392971498929017818237394074266448467963648845725270238638741470530326527225591470945568628357663345362977083408459035746665948779559824189070193446347235731566688204757001867451307179564783577100125355658166518394135392082890798973020986161756145194380336
简单来说的是按照如下方式进行加密:
$c = \text{pkey} + d^2 \quad (\text{pad}(m)) \quad \text{mod}(10^d)$
这里主要是未知d,但是仔细观察题目会发现$d = len(str(pkey))$ 所以d就已知了,直接解即可
exp:
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
Mashy
题目描述:1
Mashy may seem like a simple cracking task, but you'll need to open your eyes to identify the right things to crack.
题目:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
from hashlib import md5
from binascii import *
from secret import salt, flag
def die(*args):
pr(*args)
quit()
def pr(*args):
s = " ".join(map(str, args))
sys.stdout.write(s + "\n")
sys.stdout.flush()
def sc():
return sys.stdin.buffer.readline()
def xor(s1, s2):
return bytes([s1[_] ^ s2[_] for _ in range(len(s1))])
def main():
border = "┃"
pr( "┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓")
pr(border, ".: Hi all, she did Mashy, you should do it too! Are you ready? :. ", border)
pr( "┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛")
REC = []
cnt, STEP = 0, 7
sh = md5(salt).digest()
while True:
pr(border, f'Please send your first input: ')
d1 = sc().strip()
pr(border, f'Please send your second input: ')
d2 = sc().strip()
try:
d1 = hexlify(unhexlify(d1))
d2 = hexlify(unhexlify(d2))
h1 = md5(unhexlify(d1)).digest()
h2 = md5(unhexlify(d2)).digest()
except:
die(border, 'Your inputs are not valid! Bye!!!')
if d1 != d2 and d1 not in REC and d2 not in REC:
if md5(xor(d1, d2)).hexdigest() != 'ae09d7510659ca40eda3e45ca70e9606':
if hexlify(xor(xor(h1, h2), sh)) == b'a483b30944cbf762d4a3afc154aad825':
REC += [d1, d2]
if cnt == STEP:
die(border, f'Congrats! the flag: {flag}')
pr(border, 'Good job, try next level :P')
cnt += 1
else:
die(border, 'Your input is not correct! Bye!')
else:
die(border, 'No this one! Sorry!!')
else:
die(border, 'Kidding me!? Bye!!')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
简单来说是要完成七轮挑战,使得输入的两个16进制串d1,d2,使得满足:
- d1 不等于 d2
- d1 xor d2 的md5不为 ae09d7510659ca40eda3e45ca70e9606
- md5(d1) xor md5(d2) xor sh 的值为 a483b30944cbf762d4a3afc154aad825
这题纯出题人脑子有病,出的莫名其妙的,全靠猜
ae09d7510659ca40eda3e45ca70e9606的原像为:b’\x00’ * 256
a483b30944cbf762d4a3afc154aad825的原像为:emelinjulca
然后我们不知道salt也就是sh,就进行不下去了,其实sh就是emelinjulca,纯就跟出题人脑袋相接才能做
(ps; 赛中的时候我人都傻了,然后一看几十解了,就拿emelinjulca试了一下结果真是,真是无了大语了)
到这里问题就简单了,整几组前缀进行MD5碰撞就完事了
1 | from pwn import * |
Beheaded$
题目描述:
1 | The beheaded flags have had their headers removed, making them encrypted. Can a living entity truly survive without a head? |
题目:
1 |
|
题目将flag串写在图片上,然后对这张图片进行ECB加密,最后得到密文文件。
这个不太会,看春哥说是用工具,以后再说吧。
Medium
Alilbols
题目:
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 |
output:
1 | h = 1051643987107349427988807326909852110640860009433515828832892541964729933410444984350917250524103015414239941369074041041830326426044333499878031164851095096864048639115431370526747014210332286314344073411522846701723463410585601251886732229726828022089809603850477551571014006202841406236367999378786782206165205893353928598469661871284779486855440579818275314024966224282757807716013799903830828885606714972634243850947534165272668985513949964901606268939300116019465522042467054120201087606016018354238401711720121586874288767235317479748890350702705575809130664969776549574720593740409234863974057904204809404816059921579771581800937241591669455683460570640868196509926763901079838233646036933530095891316054589051458146768287967886035091641162494322987627448810201550901588438560433001422233269632915351406169253963308421081459981594969405377353502889363324282815864766827664453823780238352371809048289845094882346227809082005375092441877966603138648719670349093616548820955566204871333952902983753935678447080673827214244142614295192263451840766771122229866931492260663320087497820892824540996643905125018452302747847009 |
密钥生成有:
- $ 1 \leq f < \sqrt{2} \cdot 10 ^ d$
- $ 10 ^ d \leq g < \sqrt{2} \cdot 10 ^ d$
- $ q = 4 \cdot 10 ^ 2d$
- $ h = f ^ {-1} g \ (mod \ q)$
加密有:
- 取一个随机数r, 满足 $ 1 < r < \frac{10^d}{2}$
- 计算密文 $ c = rh + m + r \ (mod \ q) $
给出了h,c, 需要还原m
很明显是NTRU,直接造格:
$\begin{bmatrix} r & -1 & k \end{bmatrix}$ = $\begin{bmatrix} r & -1 & -m \end{bmatrix}$
但是我们不知道d,q, 所以需要枚举一下d的大小
exp:
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
Ally*
题目描述:
1 | Ally enjoys the challenge of solving Diophantine equations, so help them tackle this latest complex equation as well. |
题目:
1 | import sys |
- 就是给出19对如下的丢番图方程的正整数解:
赛中没做出来,赛后发现其实:
就可以了
exp:
1 | from pwn import * |
Bada*
题目描述:
1 | The Bada equation contains an undetermined function. By closely examining how this equation behaves, you may be able to discover the concealed flag. |
题目:
存在一个函数方程f: N×N → Z:
- $ f(a+1,b) = f(a,b) + a $
- $ f(a,b+1) = f(a,b) - b $
给定了f($x_0$,$y_0$)的函数值,以及f(x,y)的值,求(x,y)使满足f(x,y)=z
很明显这两个函数方程可以看作两个等差数列,也就是有:
即是:
记f(1,1)为c
也就是有:
这里就把问题变成了解关于x和y的不定方程的问题:
exp:
1 | from Pwn4Sage.pwn import * |
Duzly$
题目描述:
1 | Duzly is a straightforward hash function design based on congruence relationships over a prime number modulus. |
题目:
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
赛中看0解(自知之明一手)就没看,赛后一看果然没看懂
这里贴一下大佬的做法这里
Forghan*
题目描述:
1 | The Forghan, the combination of RSA and DLP cryptography, may in certain instances prove more accessible than employing either method individually. |
题目:
1 | import sys |
题目有三个选项,但是显然是有顺序的,具体来说应该按照下面来:
- 选择”S”,输入256bit的素数p、q
- 选择”G”,靶机对flag进行加密,加密流程如下:
- 生成n,n = (p^2 - 1) * (q^2 - 1)
- 分别生成p、q下的一个随机二次非剩余gp、gq
- 生成p、q下的随机数sp、sq
- 将flag分为两段,记为flagp、flagq,对应数字记为mp、mq
- 计算yp、yq, $y_p = g_p^{s_p} \pmod{p}$,$y_q = g_q^{s_q} \pmod{q}$
- 计算密文cp、cq,$c_p = m_p^{y_p} \pmod{n}$ ,$c_q = m_q^{y_q} \pmod{n}$
选择”P”,获取gp、gq、yp、yq的值
由于有 $y_p$、$y_q$,所以这里就变成了解一个RSA的问题,由于flag是静态的,所以可以放在一个子群里去求解,放在模p-1下有:
由于p和q都是自己构造的,很容就能得到p-1的分解,就可以解RSA解出mp、mq在p-1下的值,又因为flag是静态的,所以完全可以多次交互求crt
exp:
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
Honey
题目描述:
1 | Honey is a concealed cryptographic algorithm designed to provide secure encryption for sensitive messages. |
题目:
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import * |
params_enc.txt:
1 | p = 10580731215444436219213907263947534038012197972307836319229421193761088798378768844649759133142120180834573817149711299466707823017636232456526471274387917 |
题目给了d组如下等式:
c、Q、R、S均已知,要求还原m。同时,每次的$r_i$、$s_i$都是d bit的数,p是512bit。
由列表长度可以知道d就是32,所以r、s都是很小的量,因此自然想到消去m做一个HNP。取第0组和第1组的等式统一$m$$的系数然后做差即可:
到这就消去了m,造个格子求一下u和v即可, 这里由于u和v太小了所以一组就能求出来,正常需要多组才会准确。
exp:
1 | #sage |
Joe-19
题目描述:1
Joe-19 is a cryptographic system that leverages a top-secret version of GPT AI technology to develop advanced and robust cryptographic tools.
题目:
1 | #!/usr/bin/env sage |
output.txt:1
2n = 8098851734937207931222242323719278262039311278408396153102939840336549151541408692581651429325092535316359074019383926520363453725271849258924996783681725111665666420297112252565291898169877088446887149672943461236879128453847442584868198963005276340812322871768679441501282681171263391133217373094824601748838255306528243603493400515452224778867670063040337191204276832576625227337670689681430055765023322478267339944312535862682499007423158988134472889946113994555274385595499503495488202251032898470224056637967019786473820952632846823442509236976892995505554046850101313269847925347047514591030406052185186963433
c = 7109666883988892105091816608945789114105575520302872143453259352879355990908149124303310269223886289484842913063773914475282456079383409262649058768777227206800315566373109284537693635270488429501591721126853086090237488579840160957328710017268493911400151764046320861154478494943928510792105098343926542515526432005970840321142196894715037239909959538873866099850417570975505565638622448664580282210383639403173773002795595142150433695880167315674091756597784809792396452578104130341085213443116999368555639128246707794076354522200892568943534878523445909591352323861659891882091917178199085781803940677425823784662
预期应该是通过枚举自然对数e的连续bit去找到对应素数,但是
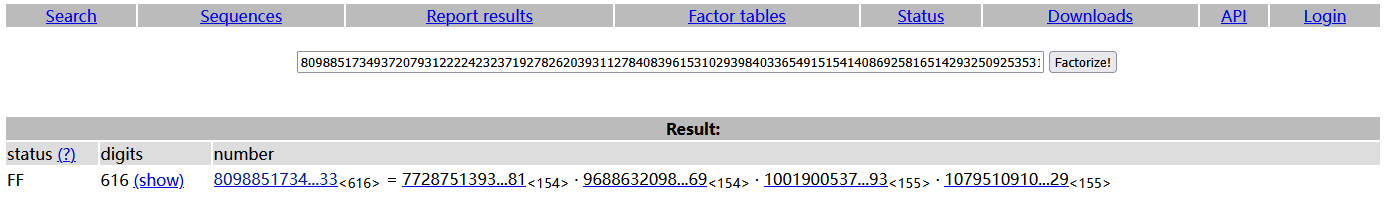
https://factordb.com/ 直接分解了那就没啥可说得了直接解RSA即可
exp:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12from Crypto.Util.number import *
n = 8098851734937207931222242323719278262039311278408396153102939840336549151541408692581651429325092535316359074019383926520363453725271849258924996783681725111665666420297112252565291898169877088446887149672943461236879128453847442584868198963005276340812322871768679441501282681171263391133217373094824601748838255306528243603493400515452224778867670063040337191204276832576625227337670689681430055765023322478267339944312535862682499007423158988134472889946113994555274385595499503495488202251032898470224056637967019786473820952632846823442509236976892995505554046850101313269847925347047514591030406052185186963433
c = 7109666883988892105091816608945789114105575520302872143453259352879355990908149124303310269223886289484842913063773914475282456079383409262649058768777227206800315566373109284537693635270488429501591721126853086090237488579840160957328710017268493911400151764046320861154478494943928510792105098343926542515526432005970840321142196894715037239909959538873866099850417570975505565638622448664580282210383639403173773002795595142150433695880167315674091756597784809792396452578104130341085213443116999368555639128246707794076354522200892568943534878523445909591352323861659891882091917178199085781803940677425823784662
p = 7728751393377105569802455757436190501772466214587592374418657530064998056688376964229825501195065837843125232135309371235243969149662310110328243570065781
q = 9688632098638681429535439991332657144752666147923336383829750592576742104399942931057096761773496510622226977570278994077236841491368959008277469453600569
r = 10019005372961705640183251650710051163228093250949727357306333102512304273058618645339800283588040423877666492199352609508401454089083503146788384653241593
s = 10795109107229646654467923653403055635071360620150038008453082390943756377071343139771120080956310498862485323957447467376538994662280143050510681877597429
m = pow(c, inverse(65537,(p-1)*(q-1)*(r-1)*(s-1)), n)
print(long_to_bytes(m))
Melek
题目描述:
1 | Melek is a secret sharing scheme that may be relatively straightforward to break - what are your thoughts on the best way to approach it? |
题目:
melek.sage:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22#!/usr/bin/env sage
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from flag import flag
def encrypt(msg, nbit):
m, p = bytes_to_long(msg), getPrime(nbit)
assert m < p
e, t = randint(1, p - 1), randint(1, nbit - 1)
C = [randint(0, p - 1) for _ in range(t - 1)] + [pow(m, e, p)]
R.<x> = GF(p)[]
f = R(0)
for i in range(t): f += x**(t - i - 1) * C[i]
P = [list(range(nbit))]
shuffle(P)
P = P[:t]
PT = [(a, f(a)) for a in [randint(1, p - 1) for _ in range(t)]]
return e, p, PT
nbit = 512
enc = encrypt(flag, nbit)
print(f'enc = {enc}')
output太长了这里就不放了,想要的去nss上下载就好
题目比较直白,建立了一个模p下的多项式f,其中加密后的flag为常数项,然后给出了t个点对,那我们只需要拉格朗日插值即可
exp:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12from Crypto.Util.number import *
from gmpy2 import *
e,p,PT = eval(open("output.txt","rb").read()[5:])
P.<x> = PolynomialRing(Zmod(p))
f = P.lagrange_polynomial(PT)
c = f(0)
m2 = pow(c,inverse(e//2,p-1),p)
ff = x^2 - m2
res = ff.roots()
print(long_to_bytes(int(res[1][0])))
Nabat
题目描述:1
Nabat is a cryptographic challenge that explores the representation of polynomials within a specific polynomial ring structure.
题目:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60#!/usr/bin/env sage
import sys
from flag import flag
def die(*args):
pr(*args)
quit()
def pr(*args):
s = " ".join(map(str, args))
sys.stdout.write(s + "\n")
sys.stdout.flush()
def sc():
return sys.stdin.buffer.readline()
def randstr(l):
return ''.join([printable[randint(0, 90)] for _ in range(l)])
def check(f, l):
R = PolynomialRing(ZZ, 'x')
f, g = R(f), R(x^2 + x + 2)
coefs = f.list()
_b1 = all(abs(_) <= 1 for _ in coefs)
_b2 = f.degree() + 1 - 2 * n(log(l)) >= 0
_b3 = coefs.count(0) >= 2 * f.degree() // 3 - 3
_b4 = (f - l) % g == 0
if _b1 and _b2 and _b3 and _b4:
return True
return False
def main():
border = "┃"
pr( "┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓")
pr(border, "Welcome to the NABAT challenge, your mission is to validate the main", border)
pr(border, "check function in the provided system, Try your best to find flag :)", border)
pr( "┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛")
step = 12
R = PolynomialRing(ZZ, 'x')
pr(border, f"Send a polynomial that satisfies the check function for each given `n'.")
for i in range(1, step):
n = randint(2**i, 2**(i + 1))
pr(border, f"Your are in step {i} and n = {n}, please send the polynomial f:")
_f = sc().decode()
try:
_f = R(_f)
except:
die(border, f"The polynomial you provided is is not valid!")
_b = check(_f, n)
if _b:
if i == step - 1:
die(border, f'Congrats, you got the flag: {flag}')
else:
pr(border, f'You have successfully passed step {i}. Please proceed to the next step :)')
else:
die(border, f"Your input does not meet the requirements!!!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
一共有12轮挑战,每轮生成一个n(随轮数增大而增大),我们需要提交一个多项式并且满足:
- 所有的系数的绝对值都≤1
- 多项式的度$d$要≥$2longn - 1$
- 系数为0的数量要≥$[ \frac {3}{2d} ] - 3$
- $f-n$ 能被$g$整除
其中$g=x^2+x+2$